The Enchanting World of Morel Mushrooms: Types, Benefits, and Safe Usage 🍄✨
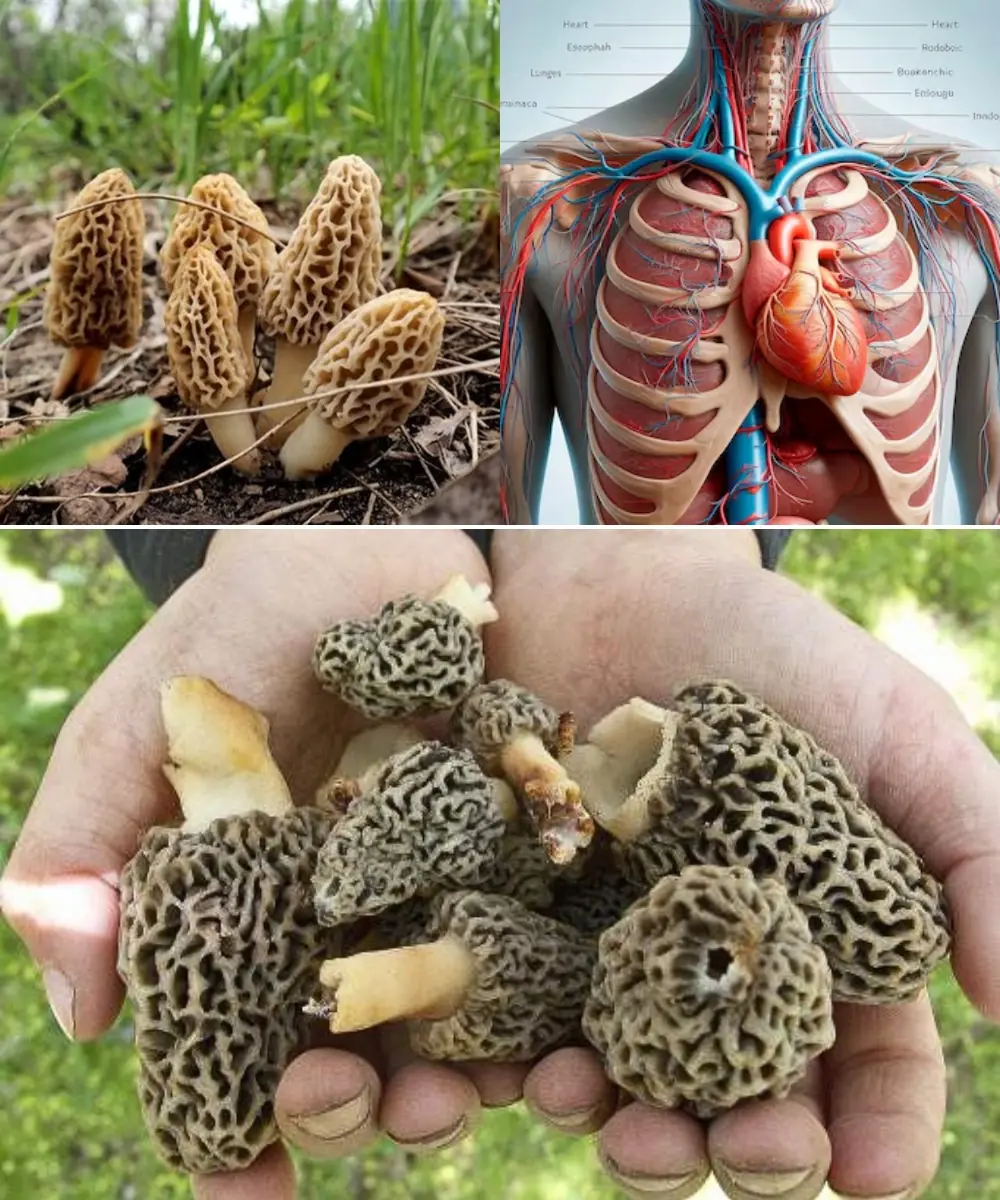
Morel mushrooms (Morchella spp.) are among the most coveted wild mushrooms, prized for their rich, earthy flavor and meaty texture. These elusive fungi are not only a gourmet delicacy but also boast numerous health benefits. Whether you’re a forager, a food lover, or a health enthusiast, understanding morels’ types, benefits, and safe usage can enhance your appreciation of these fascinating fungi.
Types of Morel Mushrooms
Morel mushrooms come in various species, but the most common ones include:
1. Black Morels (Morchella elata & Morchella angusticeps)
- Dark, wrinkled caps with deep ridges
- Found in burn sites, forests, and near decaying trees
- Rich, smoky flavor, perfect for sautéing
2. Yellow Morels (Morchella esculenta)
- Light golden to tan color with a honeycomb structure
- Grows in deciduous forests, near elm, ash, and apple trees
- Mild, nutty taste, great for soups and sauces
3. Half-Free Morels (Morchella semilibera)
- Cap attached only halfway to the stem
- Found in moist wooded areas and riverbanks
- Less flavorful but still edible when cooked
Health Benefits of Morel Mushrooms
1. Rich in Nutrients
Morels are packed with essential vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin D – Supports bone health and immunity
- Iron – Aids red blood cell production
- Antioxidants – Helps fight oxidative stress
2. Boosts Immunity
Morels contain beta-glucans, which enhance immune function and help the body fight infections.
3. Supports Brain Health
Rich in polyphenols and micronutrients, morels may protect against cognitive decline and support mental clarity.
4. Aids Digestion
High in fiber, morels promote gut health and improve digestion.
5. Potential Anti-Cancer Properties
Studies suggest that morels may contain compounds with anti-cancer properties, though more research is needed.
Safe Usage: How to Harvest & Cook Morels
1. Identifying Edible vs. False Morels
- True Morels: Hollow from stem to cap, honeycomb-like texture
- False Morels (Gyromitra spp.): Dense, irregularly shaped, can be toxic if consumed
2. Cooking Morels Properly
Never eat raw morels—they contain hydrazine toxins, which can cause digestive upset.
- Rinse well to remove dirt and insects
- Sauté in butter, olive oil, or cream sauces for a rich, umami flavor
- Pair with meats, eggs, pasta, or risotto for gourmet dishes
3. Storing Morels for Longevity
- Fresh Morels: Store in a paper bag in the fridge for up to 1 week
- Dried Morels: Last months to years when stored in an airtight container
- Frozen Morels: Blanche first and store for long-term use
Final Thoughts
Morel mushrooms are a true culinary treasure, offering a unique flavor profile and a variety of health benefits. Whether you’re foraging in the wild or purchasing them from a specialty store, always ensure proper identification, cooking, and storage for a safe and delicious experience. Ready to explore the magic of morels? Morel mushrooms (Morchella spp.) are among the most coveted wild mushrooms, prized for their rich, earthy flavor and meaty texture. These elusive fungi are not only a gourmet delicacy but also boast numerous health benefits. Whether you’re a forager, a food lover, or a health enthusiast, understanding morels’ types, benefits, and safe usage can enhance your appreciation of these fascinating fungi.
Types of Morel Mushrooms
Morel mushrooms come in various species, but the most common ones include:
1. Black Morels (Morchella elata & Morchella angusticeps)
- Dark, wrinkled caps with deep ridges
- Found in burn sites, forests, and near decaying trees
- Rich, smoky flavor, perfect for sautéing
2. Yellow Morels (Morchella esculenta)
- Light golden to tan color with a honeycomb structure
- Grows in deciduous forests, near elm, ash, and apple trees
- Mild, nutty taste, great for soups and sauces
3. Half-Free Morels (Morchella semilibera)
- Cap attached only halfway to the stem
- Found in moist wooded areas and riverbanks
- Less flavorful but still edible when cooked
Health Benefits of Morel Mushrooms
1. Rich in Nutrients
Morels are packed with essential vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin D – Supports bone health and immunity
- Iron – Aids red blood cell production
- Antioxidants – Helps fight oxidative stress
2. Boosts Immunity
Morels contain beta-glucans, which enhance immune function and help the body fight infections.
3. Supports Brain Health
Rich in polyphenols and micronutrients, morels may protect against cognitive decline and support mental clarity.
4. Aids Digestion
High in fiber, morels promote gut health and improve digestion.
5. Potential Anti-Cancer Properties
Studies suggest that morels may contain compounds with anti-cancer properties, though more research is needed.
Safe Usage: How to Harvest & Cook Morels
1. Identifying Edible vs. False Morels
- True Morels: Hollow from stem to cap, honeycomb-like texture
- False Morels (Gyromitra spp.): Dense, irregularly shaped, can be toxic if consumed
2. Cooking Morels Properly
Never eat raw morels—they contain hydrazine toxins, which can cause digestive upset.
- Rinse well to remove dirt and insects
- Sauté in butter, olive oil, or cream sauces for a rich, umami flavor
- Pair with meats, eggs, pasta, or risotto for gourmet dishes
3. Storing Morels for Longevity
- Fresh Morels: Store in a paper bag in the fridge for up to 1 week
- Dried Morels: Last months to years when stored in an airtight container
- Frozen Morels: Blanche first and store for long-term use
Final Thoughts
Morel mushrooms are a true culinary treasure, offering a unique flavor profile and a variety of health benefits. Whether you’re foraging in the wild or purchasing them from a specialty store, always ensure proper identification, cooking, and storage for a safe and delicious experience. Ready to explore the magic of morels?
News in the same category


The Best Cooking Fats: What to Use and What to Avoid 🧈🔥

Permanent Rat Removal: Natural and Effective Solutions
Unlocking the Health Benefits of Cayenne Pepper, Olive Oil, and Lemon Juice

11 Reasons Why You Should Drink Aloe Vera Water Every Day

Do This Before Bed: The Overnight Remedy to Combat Candida and Fungi

Lose Weight in 7 Days Forever! Melt Belly & Hip Fat with Cinnamon & Lemon

Ageratum conyzoides (Billygoat Weed): 15 Incredible Benefits and How to Use It

The Powerful Plant That May Aid Wellness: Exploring the Benefits of Greater Burdock Root
The Incredible Health Benefits of Dates: Nature’s Sweet Superfood

Chayote-Based Remedies for Better Health: 3 Natural Recipes 🌿🍋

Hospitals Emptied: This Drink Cures Poor Circulation, Diabetes, and High Blood Pressure Without Taking Pills

Hidden Uses of Scent Leaf You Probably Didn’t Know!

The Best Benefits of Combining Coffee and Garlic: A Powerful Duo for Health
Kills Nail Fungus Instantly! The Best Aloe Vera Remedy
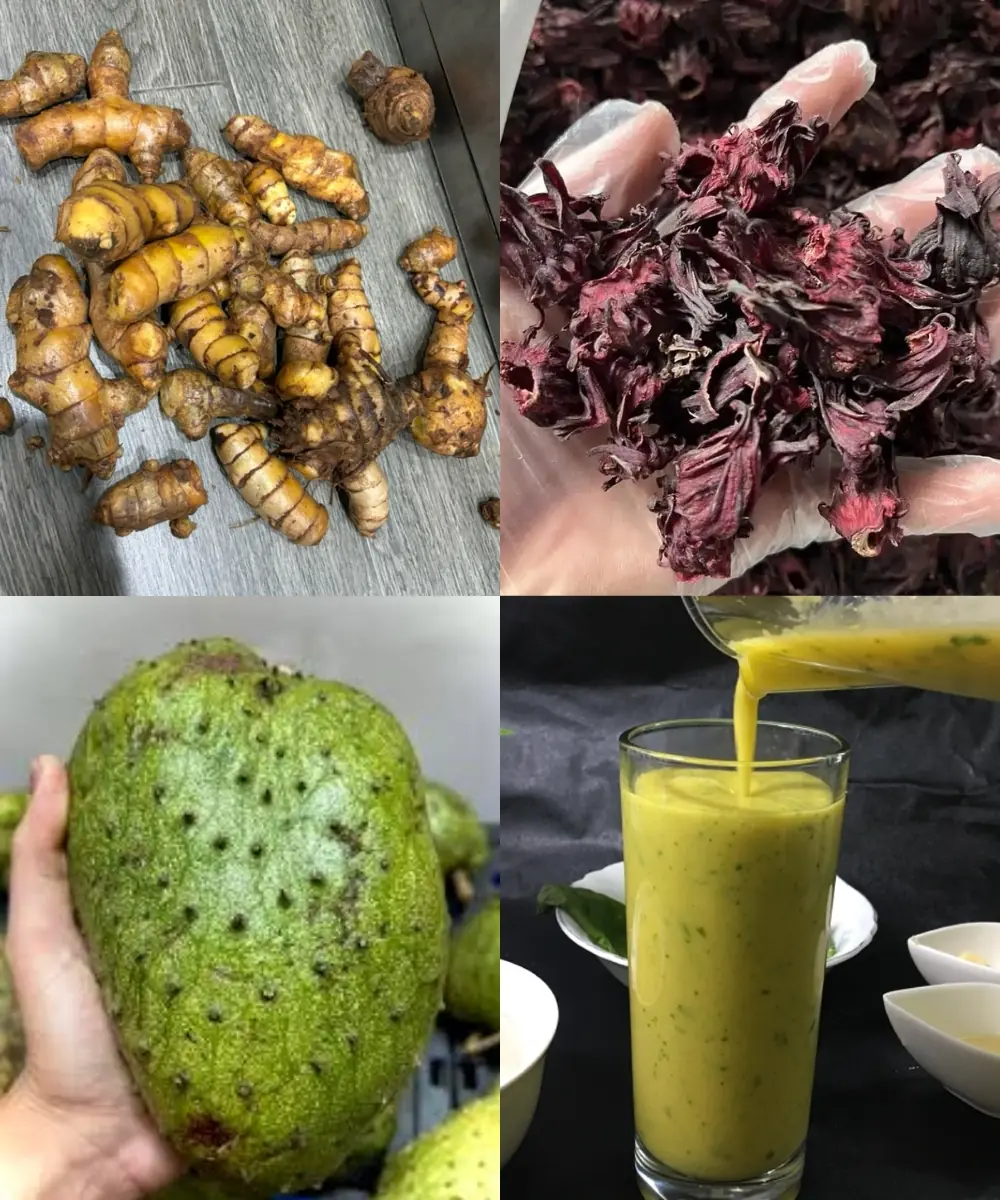

The Drink That Will Keep Hospitals Empty in 2025! A Natural Remedy for Diabetes, High Blood Pressure & More
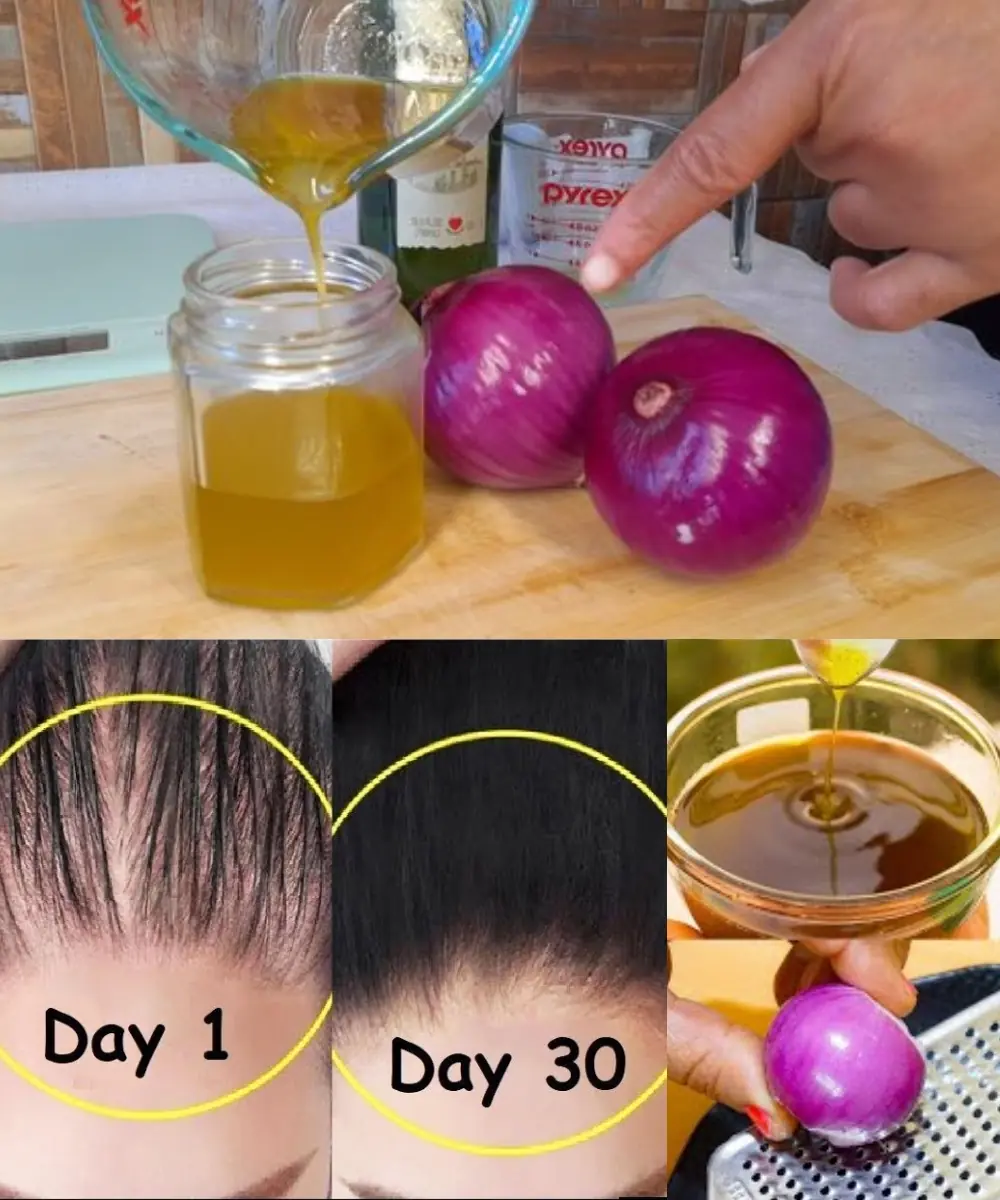

How to Make Onion Hair Oil for Faster Hair Growth and to Stop Hair Fall
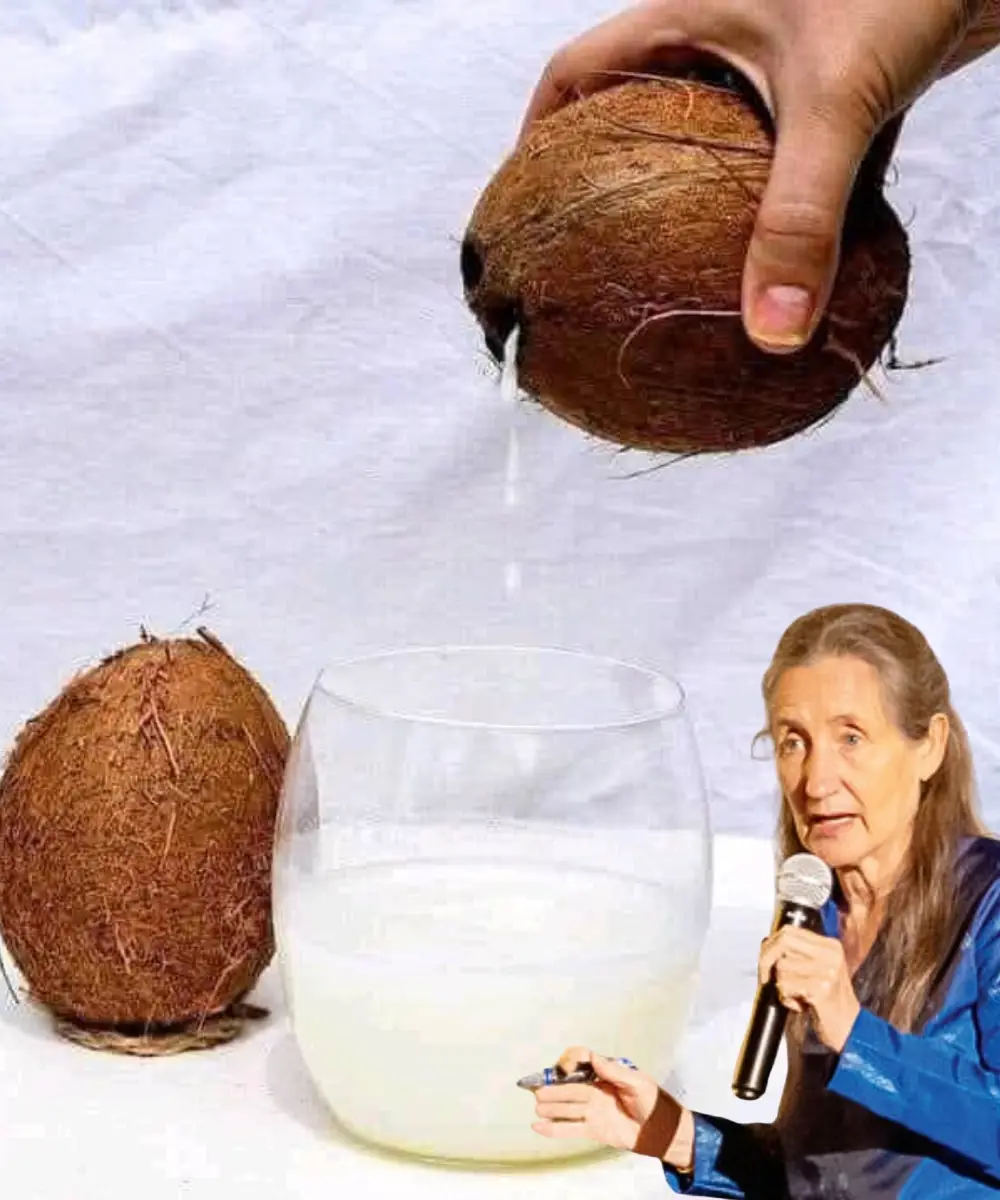

Don't Drink Coconut Water Before Doing These 3 Things! ⚠️🥥
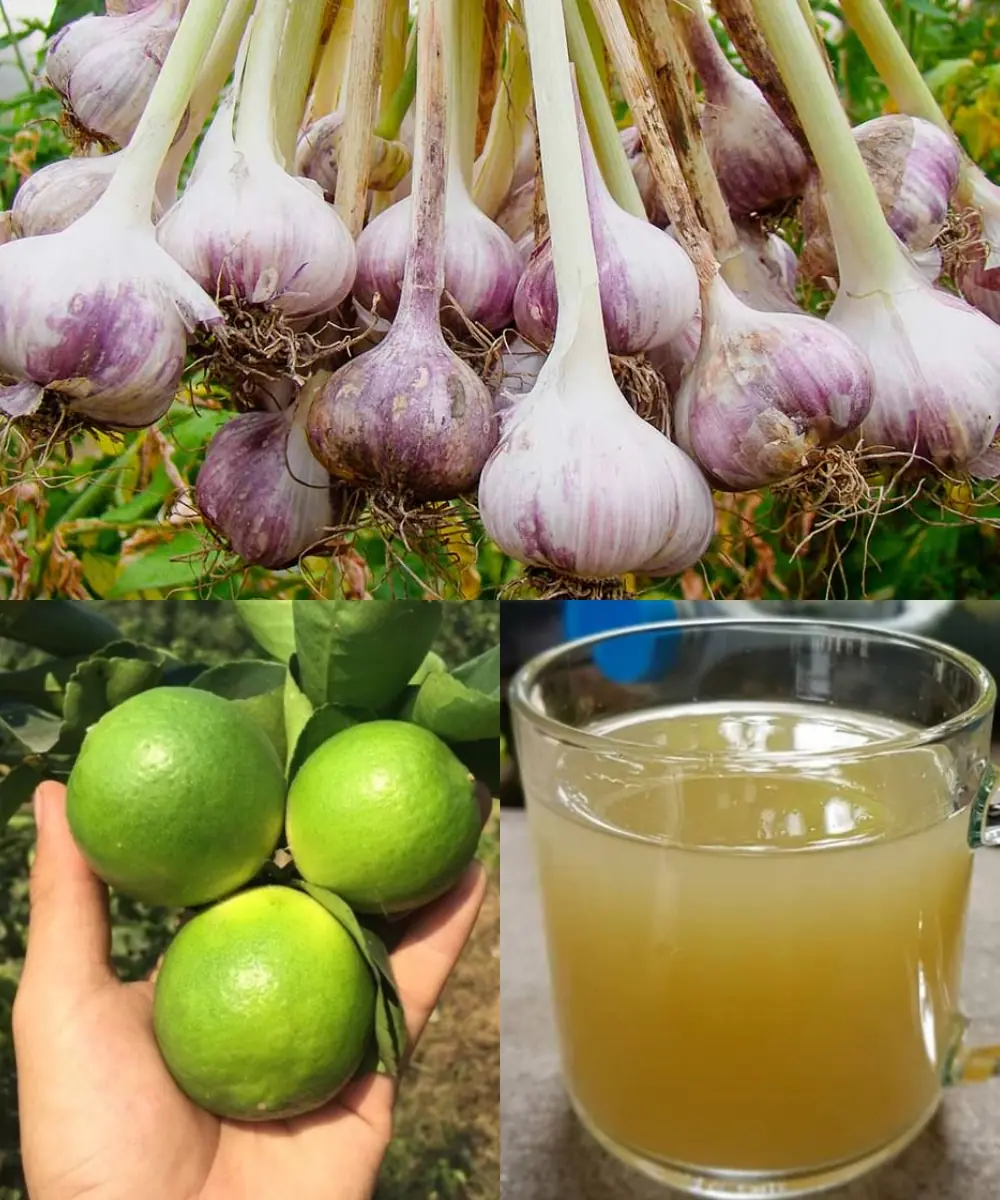

Boost Your Energy and Confidence with This All-Natural Drink
News Post

Tips for choosing ripe watermelons with red flesh, sweet, and paper-thin flesh
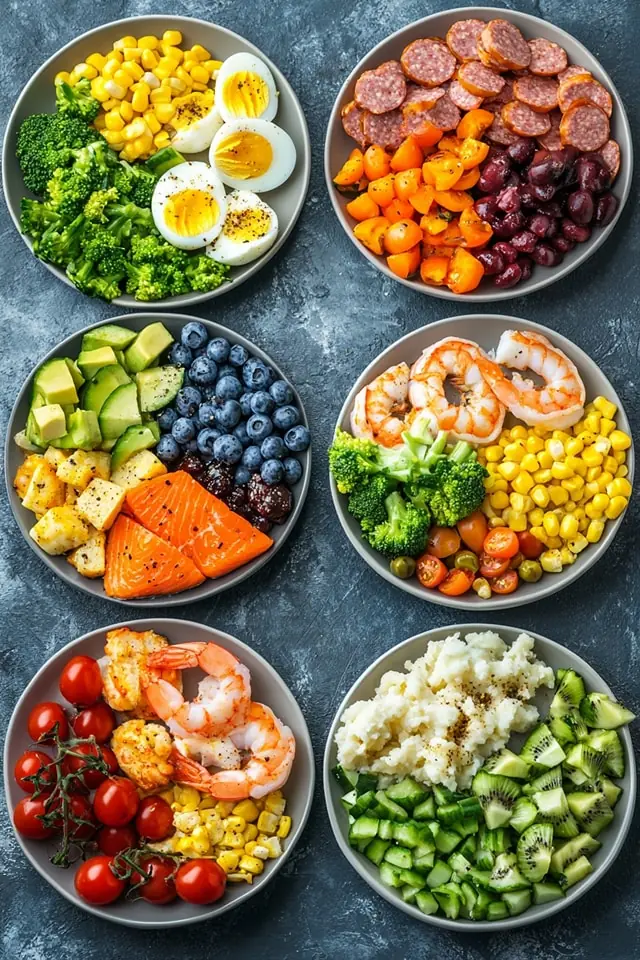

6 Nutritious & Delicious Meal Ideas for a Healthy Lifestyle 🍽️🥑🥦🍤

Healthy & Delicious Meal Ideas for the Whole Week 🥑🍅🥦🥕🥬

Crunchy Apple & Carrot Salad with Creamy Citrus Dressing

6 Powerful Juice Recipes for a Healthier You! 🥤✨

Morning Detox: Start Your Day with Lime Water & Black Seed Oil 🍋✨
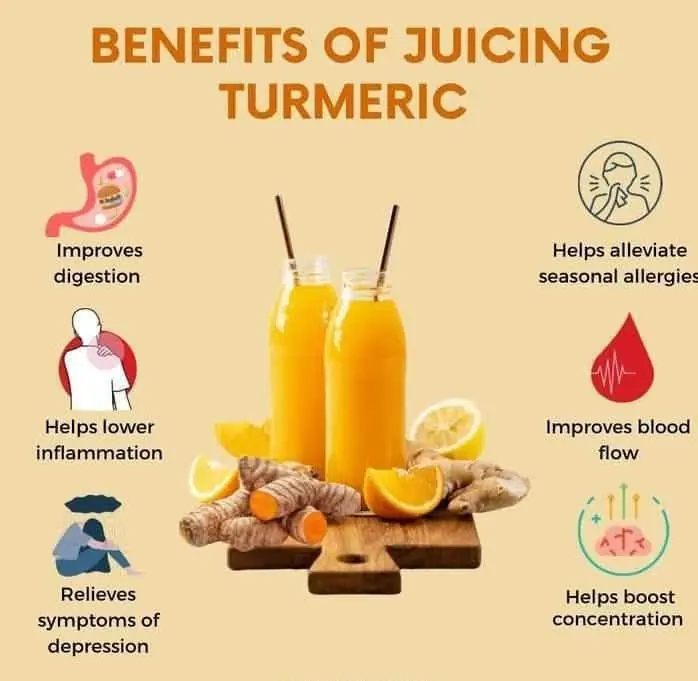
Turmeric Juice: The Golden Elixir for Your Health 🌿✨

Cheesy Garlic Chicken Wraps
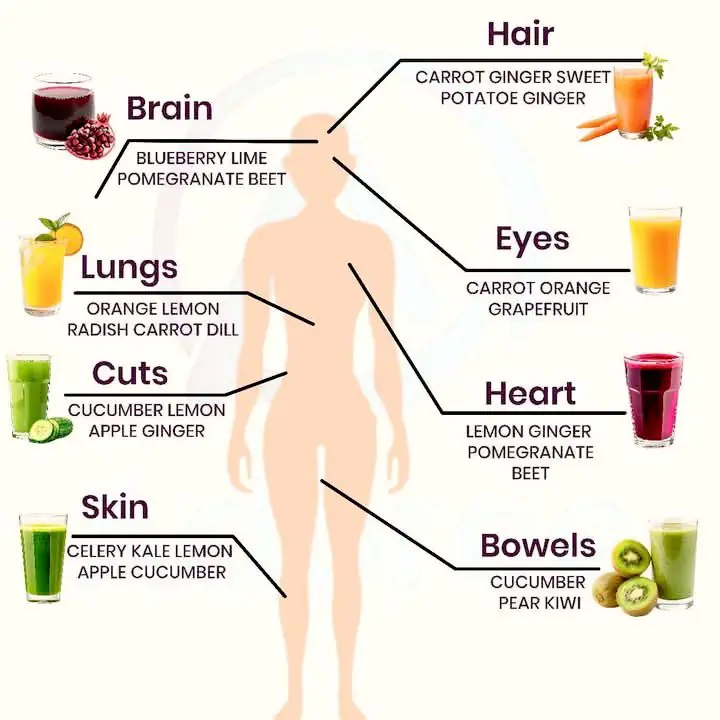
Juices for a Healthier Body: Boost Every Part of Your Health Naturally! 🥤✨

Crispy Bang Bang Salmon Bites
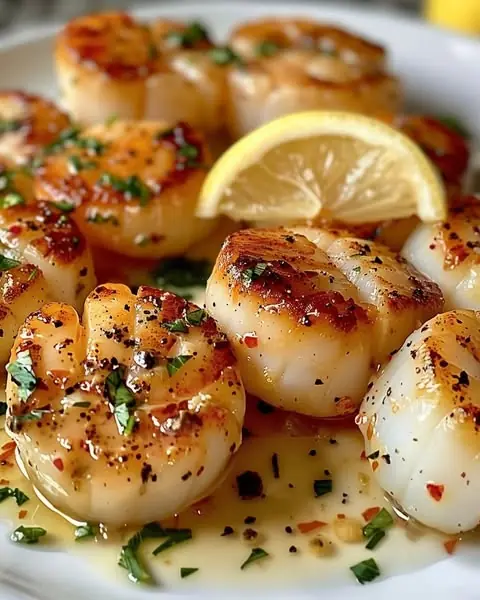

Garlic Butter Lobster and Scallops

Anti-Aging Smoothie: A Delicious and Nutritious Recipe for Youthful Glow ✨🍓

Fluffy Bao Buns Recipe

Easy Strawberry Crunch Recipe ⬇️
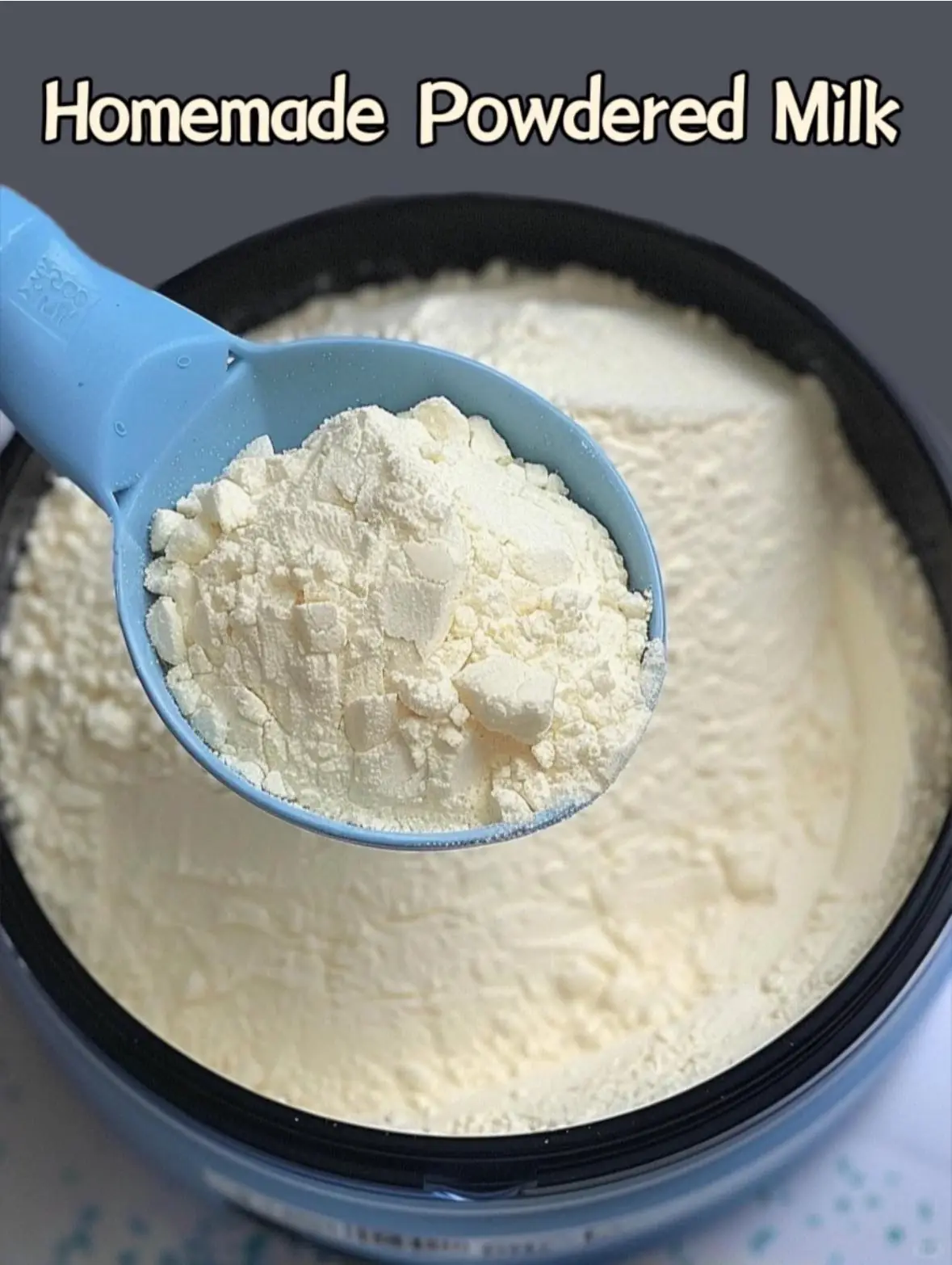

How to Make Powdered Milk at Home ⬇️

The Best Cooking Fats: What to Use and What to Avoid 🧈🔥

Moist and Soft Cake (NO EGGS!!)
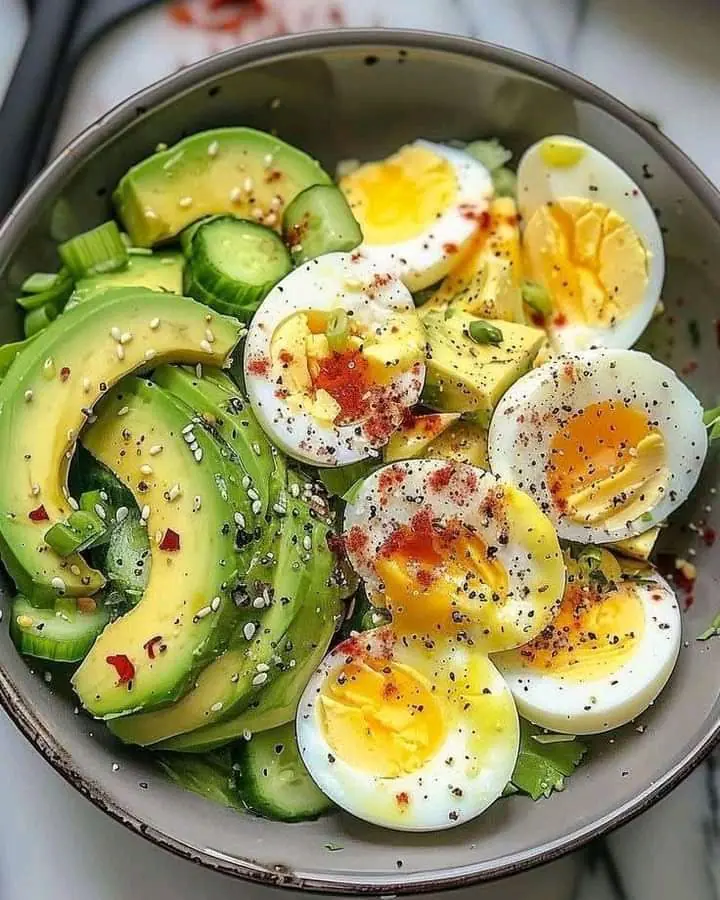

Spicy Avocado & Egg Salad Bowl

Purple Sweet Potato Balls
